
1Commerce Department, University College Benra-Dhuri (A constituent college of Punjabi University), Patiala, Punjab, India
2Department of Commerce, Punjabi University, Patiala, Punjab, India
Creative Commons Non Commercial CC BY-NC: This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 License (http://www.creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) which permits non-Commercial use, reproduction and distribution of the work without further permission provided the original work is attributed.
Objectives: This study examines the influence of fintech innovations on investors’ decision-making and behavior in mutual fund investments.
Methodology: The study reviews studies published between 2008 and 2024 across databases such as Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar using a systematic literature review (SLR) approach.
Findings: Fintech solutions have been shown to significantly enhance investor convenience, accessibility, and engagement by lowering barriers to entry and facilitating real-time financial insights. Blockchain technology promotes trust and transaction security, while robo-advisors and artificial intelligence (AI)-based analytics offer tailored portfolio recommendations. However, even in digital environments with abundant data, behavioral biases such as herding and overconfidence still influence decision-making.
Implications: According to the research, adopting fintech into mutual fund ecosystems can boost investor confidence, encourage transparent investing practices, and improve financial inclusion. To promote sustainable fintech adoption, policymakers, and financial institutions aim to develop regulatory frameworks that ensure investor awareness, ethical AI use, and data protection.
Fintech, Mutual Funds, Robo-Advisors, Blockchain, Big Data Analytics, Investor Behavior
Introduction
Fintech developments have brought out a new era of communication between investors and financial markets, significantly changing the economic landscape in India. From the words “financial” and “technology,” the term “fintech” refers to a range of digital tools and apps for financial services that facilitate easier, more convenient, and more decision-friendly transactions.
Fintech advances largely determine behavior, which in turn influences market dynamics. The innovation makes investments more accessible and transparent by removing obstacles, including information asymmetry, procedural complexity, and a lack of financial literacy. Furthermore, to develop individualized financial solutions, fintech platforms examine investor preferences and risk tolerance using artificial intelligence (AI) and big data analytics.
The digital revolution, driven by the convergence of financial services and rapidly advancing technologies, has had a big impact on how investors participate in mutual funds globally. Fintech technologies have changed investor behavior, increased accessibility, and improved efficiency, revolutionizing traditional investing procedures. The mutual fund sector in India exemplifies this shift, with assets under management (AUM) increasing from .png) 27.05 trillion in 2019 to
27.05 trillion in 2019 to .png) 68.08 trillion in 2024, primarily driven by systematic investment plans (SIPs) and digital adoption.
68.08 trillion in 2024, primarily driven by systematic investment plans (SIPs) and digital adoption.
The study examines how fintech significantly shapes investor behavior in mutual funds. It investigates how technological advancements affect financial involvement, trust, and investment choices.
In the current financial landscape, it is essential to examine how fintech affects mutual fund investments as it reflects the ongoing shift in how investors access, assess, and manage financial assets in an increasingly digital market. By improving transparency, simplicity, and personalization, fintech innovations like robo-advisors, blockchain, AI-driven analytics, and mobile trading platforms have completely changed the way mutual funds are distributed. Fintech acts as a catalyst for financial inclusion, investor education, and operational efficiency in India, where mutual fund AUMs keep growing rapidly.
There are notable gaps in the current research on how fintech affects mutual fund investing. Most studies focus on financial technologies broadly rather than the specific dynamics related to mutual funds, and little research examines how investor behavior shifts with fintech adoption. Additionally, limited work has been done on how fintech interacts with traditional mutual fund distributors or influences different investor segments. These gaps emphasize the need for more comprehensive, long-term, and focused studies to understand how fintech is changing mutual fund investment methods.
Literature Review
Fintech has shifted investor preferences to direct plan investments, eschewing middlemen in favor of more efficiency and transparency. Investors make frequent, well-informed decisions by utilizing goal-based recommendation tools, SIPs, and real-time data. Although behavioral biases still exist, trust and literacy are strengthened by digital transparency and personalized data.
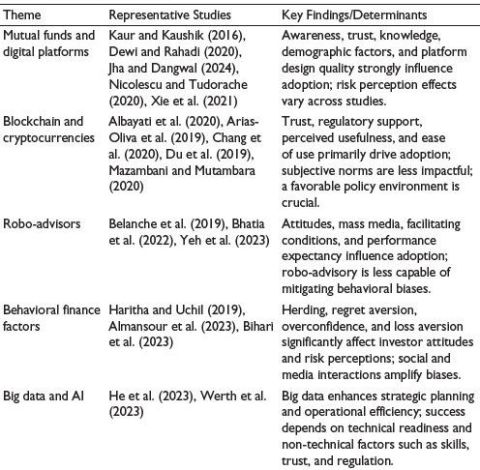
Mutual Funds and Digital Platforms
Millennials and Gen Z are increasingly using digital platforms for investing in mutual funds. Kaur & Kaushik (2016) and Kaur (2018) revealed that while risk perception is less important, awareness has a significant impact on decisions. Dewi and Rahadi (2020) found that Indonesian millennials are influenced by design quality and trust. For Gen Z investors in India, Jha and Dangwal (2024) highlighted perceived risk, pricing value, and service trust as factors. Similar findings on platform usability and adoption behavior are also reported by Xie et al. (2021).
Behavioral and Technological Determinants
When it comes to fintech adoption, behavioral biases continue to play a significant role. Almansour et al. (2023) demonstrated how disposition effects, blue-chip bias, and herding influence investor attitudes and risk-taking. Bihari et al. (2023) identified regret aversion and overconfidence as two significant biases that were exacerbated by the handy features of fintech. Haritha and Uchil (2019) provided evidence that peer and media influences predominate in decision-making, which is consistent with behavioral finance theory (Badola et al., 2023). A systematic synthesis of behavioral biases affecting investment decisions further supports these findings (Badola et al., 2023).
Blockchain and Cryptocurrencies
Blockchain’s immutability, transparency, and decentralization have sparked interest in its implementation, particularly for safeguarding and resolving issues in mutual fund operations. Albayati et al. (2020) highlight the importance of supportive policy frameworks for investor acceptability, emphasizing trust and regulatory clarity. Arias-Oliva et al. (2019) integrate technology acceptance model (TAM) with financial literacy and perceived risk, highlighting performance expectancy as a greater driver. Mazambani and Mutambara (2020) showed, using theory of planned behavior (TPB) in South Africa, that attitudes and perceived behavioral control have a more significant influence on bitcoin acceptance than subjective norms.
Robo-advisors
Robo-advisors provide affordable, algorithmic investment techniques, democratizing portfolio management (Belanche et al., 2019). Although robo-advisors improve access, they might not be able to eliminate abnormal behaviors as biases such as overconfidence and loss aversion still exist in automated systems (Bhatia et al., 2022). Yeh et al. (2023) showed that facilitating conditions and performance expectations directly influence the behavioral intention.
Big Data and AI
Not only does dig data analytics improve portfolio optimization and forecast accuracy, but it also requires ethical frameworks, expertise, and organizational readiness (He et al., 2023; Lee & Lee, 2015). Although its use raises concerns about responsibility, privacy, and governance, AI is transforming risk management, investor profiling, and regulatory compliance in the mutual fund industry.
Industry Trends and Growth
An overview of prior studies examining FinTech adoption, behavioral factors, and mutual fund investments is presented in Table 1. Empirical data support the global growth in mutual funds made possible by fintech. According to the International Investment Funds Association (n.d.), with consistent inflows, regulated open-end funds are predicted to reach $69.17 trillion by the first quarter of 2024. In FY24, SIP investments in India totaled about .png) 2 lakh crore, demonstrating the growing integration of digital platforms. New trends indicate that digital onboarding, cybersecurity improvement, and mobile access are boosting investor participation and trust.
2 lakh crore, demonstrating the growing integration of digital platforms. New trends indicate that digital onboarding, cybersecurity improvement, and mobile access are boosting investor participation and trust.
Table 1. Overview of Studies.
Research Methodology
The Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines were followed in this study’s systematic literature review (SLR) to ensure methodological rigor, transparency, and replicability.
Search Strategy
The three main databases, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar, were thoroughly researched. Industry reports from AMFI, IIFA, and EY fintech reports were additional sources.
The following keywords were combined in search strings: “FinTech,” “mutual funds,” “robo-advisors,” “blockchain,” “investor behavior,” “AI in finance,” “digital platforms,” “technology adoption,” and “investment decisions.”
Works published between 2008 and 2024 were considered in the review.
Inclusion Criteria
Included studies were those that:
Exclusion Criteria
Excluded studies were those that:
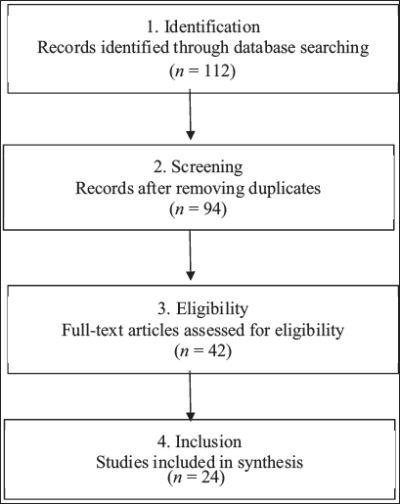
PRISMA Flow Summary
The study selection and screening process followed under PRISMA guidelines is illustrated in Figure 1.
Figure 1. A PRISMA Flow Diagram.
Research Gap
The link between fintech adoption and mutual fund investor behavior is largely overlooked, especially in India. While many studies examine fintech and investing as a whole, there is limited insight into how technologies like blockchain, AI, and robo-advisors affect behavioral biases and decision-making in mutual fund investments.
Objective
To examine how technology-driven platforms and fintech tools improve accessibility, streamline investing procedures, and affect investor behavior in mutual fund investments.
Mutual Fund Industry Growth: Empirical Trends
Growth in Mutual Fund AUM Surpassed Bank Deposits in the Last Five Years
Indian mutual fund AUM grew at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 17.5%, from .png) 23.80 lakh crore in March 2019 to
23.80 lakh crore in March 2019 to .png) 53.40 lakh crore in March 2024. In the meantime, bank deposits grew at a CAGR of 11.0%, from
53.40 lakh crore in March 2024. In the meantime, bank deposits grew at a CAGR of 11.0%, from .png) 126.39 lakh crore in March 2019 to
126.39 lakh crore in March 2019 to .png) 212.53 lakh crore in March 2024. Investor preferences have shifted because low interest rates on fixed deposits have encouraged them to consider higher-return options such as mutual funds.
212.53 lakh crore in March 2024. Investor preferences have shifted because low interest rates on fixed deposits have encouraged them to consider higher-return options such as mutual funds.
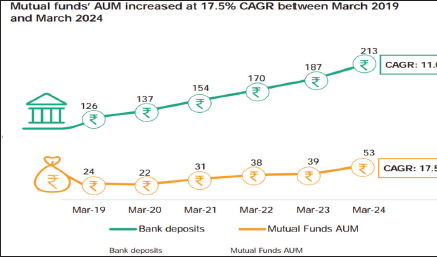
Source: Indian mutual fund industry; Association of Mutual Funds in India (AMFI, n.d.) website (www.amfiindia.com).
MF Industry’s Assets Jump
The mutual fund industry has experienced remarkable growth, with AUM rising ninefold over the past 15 years, from .png) 5.89 lakh crore in May 2008 to
5.89 lakh crore in May 2008 to .png) 53.40 lakh crore in March 2024. This significant growth reflects a shift in investor behavior and the increasing adoption of SIPs and digital platforms, underscoring the impact of fintech innovations on the mutual fund landscape. Some of the factors driving expansion include increased retail involvement, greater digital use, financial knowledge, disposable incomes, and legislative reforms that encourage competition.
53.40 lakh crore in March 2024. This significant growth reflects a shift in investor behavior and the increasing adoption of SIPs and digital platforms, underscoring the impact of fintech innovations on the mutual fund landscape. Some of the factors driving expansion include increased retail involvement, greater digital use, financial knowledge, disposable incomes, and legislative reforms that encourage competition.
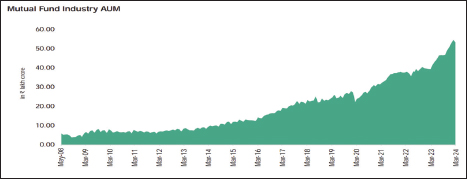
Source: Indian mutual fund industry; AMFI(n.d.) website (www.amfiindia.com).
Table 2. Conceptual Framework That Maps Fintech Dimensions to Investor Behavior Variables Such as Trust, Risk Tolerance, and Behavioral Bias.
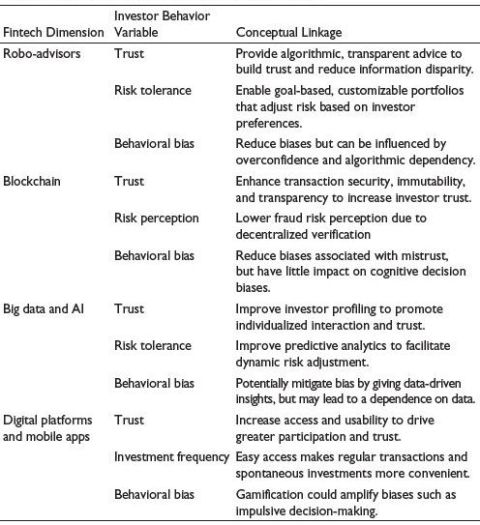
Note: This theoretical framework shows how different fintech innovations affect various aspects of investors’ behavior, including risk tolerance, trust, and behavioral bias, and how they could assist or hinder mutual fund investment decisions.
Table 3. Linking the Discussion with Behavioral Finance or Technology Adoption Theories.
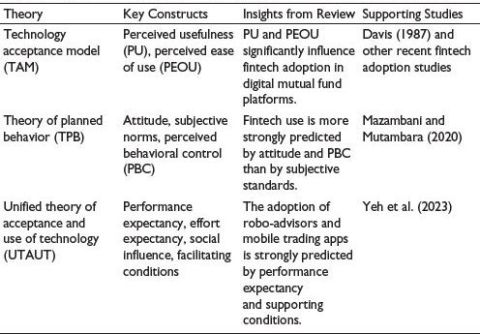
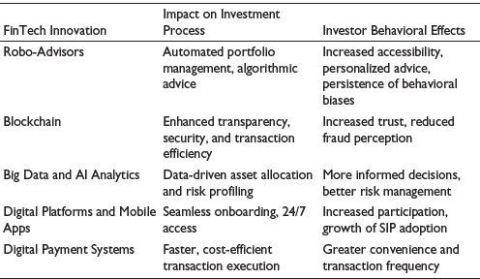
Table 4. Influence of Fintech on Mutual Fund Investments.
Discussion
The findings show that fintech significantly changes investor involvement, lowers barriers to entry, and improves transparency in mutual fund investing (Table 4). Despite advances in technology, long-standing psychological biases still influence investment behavior. The dualism implies that while technology enhances human judgment and psychological processes, it does not replace them. For fintech integration to be sustainable, inclusive technical design, policy evolution, and strategic investor education are essential.
Research such as that by Belanche et al. (2019) and Bhatia et al. (2022) demonstrates that while robo-advisors improve accessibility, biases such as loss aversion and overconfidence remain. Similarly, Albayati et al. (2020) and Mazambani and Mutambara (2020) show that blockchain adoption is more significantly influenced by regulatory clarity and trust than by technological expertise.
Comparing research shows that:
Ethical and Regulatory Challenges
Despite the advantages of fintech, many issues still exist:
To ensure responsible and inclusive fintech adoption in mutual fund ecosystems, these challenges must be addressed.
The conceptual linkage between FinTech dimensions and investor behavior variables is summarized in Table 2. Theoretical foundations explaining technology adoption and investor behavior are summarized in Table 3.
Conclusion
FinTech innovations are changing the way people participate in mutual funds by increasing investor participation, accessibility, and convenience. Technologies include mobile trading apps, blockchain platforms, robo-advisors, and big data analytics, enabling real-time data, customized recommendations, and faster transactions. However, investment behavior is still influenced by behavioral biases and regulatory constraints. To establish a transparent, safe, and inclusive investment framework, legislators, banks, and tech companies must work together. Future research should investigate how fintech impacts different investor types, ethical considerations, and the effectiveness of regulations. The influence of various FinTech innovations on the mutual fund investment process and investor behavior is presented in Table 4.
Limitations of the Study
Future Implications
Declaration of Conflicting Interests
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Funding
The authors received no financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Albayati, H., Kim, S. K., & Rho, J. J. (2020). Acceptance of financial transactions using blockchain technology and cryptocurrency: A customer perspective approach. Technology in Society, 62, 101320.
Almansour, B. Y., Elkrghli, S., & Almansour, A. Y. (2023). Behavioral finance factors and investment decisions: A mediating role of risk perception. Cogent Economics & Finance, 11(2), 2239032.
Arias-Oliva, M., Pelegrín-Borondo, J., & Matías-Clavero, G. (2019). Variables influencing cryptocurrency use: A technology acceptance model in Spain. Frontiers in Psychology, 10, 475.
Association of Mutual Funds in India (AMFI). (n.d.). Retrieved September 22, 2025, from http://www.amfiindia.com
Badola, S., Sahu, A. K., & Adlakha, A. (2023). A systematic review of behavioral biases affecting individual investment decisions. Qualitative Research in Financial Markets, 16(3), 448–476.
Belanche, D., Casaló, L. V., & Flavián, C. (2019). Artificial intelligence in fintech: Understanding robo-advisors’ adoption among customers. Industrial Management & Data Systems, 119(7), 1411–1430.
Bhatia, A., Chandani, A., Divekar, R., Mehta, M., & Vijay, N. (2022). Digital innovation in the wealth management landscape: The moderating role of robo-advisors in behavioral biases and investment decision-making. International Journal of Innovation Science, 14(3/4), 693–712.
Bihari, A., Dash, M., Muduli, K., Kumar, A., Mulat-Weldemeskel, E., & Luthra, S. (2023). Does cognitive biased knowledge influence investor decisions? An empirical investigation using machine learning and ANN. VINE Journal of Information and Knowledge Management Systems, 55(2), 445–469.
Chang, V., Baudier, P., Zhang, H., Xu, Q., Zhang, J., & Arami, M. (2020). How blockchain can impact financial services. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 158, 120166.
Davis, F. D. (1987). User acceptance of information systems: The technology acceptance model (TAM).
Dewi, E. K., & Rahadi, R. A. (2020). A conceptual study of technology adoption of an online mutual fund investment platform. European Journal of Business and Management Research, 5(3). https://doi.org/10.24018/ejbmr.2020.5.3.334
Du, W. D., Pan, S. L., Leidner, D. E., & Ying, W. (2019). Affordances, experimentation, and actualization of Fintech: A blockchain implementation study. The Journal of Strategic Information Systems, 28(1), 50–65.
Haritha, P. H., & Uchil, R. (2019). Impact of investor sentiment on decision-making in the Indian stock market: An empirical analysis. Journal of Advances in Management Research, 17(1), 66–83.
He, W., Hung, J. L., & Liu, L. (2023). Impact of big data analytics on banking. Journal of Enterprise Information Managemen, 36(2), 459-479.
International Investment Funds Association. (n.d.). Retrieved September 22, 2025, from https://iifa.ca
Jha, S., & Dangwal, R. C. (2024). Determinants of investment-related Fintech services among retail investors in India. Journal of Modeling in Management, 19(5), 1719–1747.
Kaur, I. (2018). Mutual fund behavior towards information search and selection criteria: Do knowledge and perception about mutual funds matter? Qualitative Research in Financial Markets, 10(4), 395–414.
Kaur, I., & Kaushik, K. P. (2016). Determinants of investment behavior of investors towards mutual funds. Journal of Indian Business Research, 8(1), 19–42.
Lee, I., & Lee, K. (2015). The Internet of Things (IoT): Applications, investments, and challenges for enterprises. Business Horizons, 58(4), 431–440.
Mazambani, L., & Mutambara, E. (2020). Predicting Fintech innovation adoption in South Africa: The case of cryptocurrency. African Journal of Economic and Management Studies, 11(1), 30–50.
Nicolescu, L., & Tudorache, F. G. (2020). Investment behavior in mutual funds: Is it a knowledge-based decision? Kybernetes, 50(10), 2726–2752.
Werth, O., Cardona, D. R., Torno, A., Breitner, M. H., & Muntermann, J. (2023). What determines fintech success? Electronic Markets, 33(1), 21–36.
Xie, J., Ye, L., Huang, W., & Ye, M. (2021). Understanding fintech platform adoption. Journal of Theoretical and Applied Electronic Commerce Research, 16(5), 1893–1911.
Yeh, H. C., Yu, M. C., Liu, C. H., & Huang, C. I. (2023). Robo-advisor adoption under UTAUT. Asia Pacific Journal of Marketing and Logistics, 35(4), 962–979.