
1Tantia University, Sri Ganganagar, Rajasthan, India
2Department of Commerce and Management, Tantia University, Sri Ganganagar, Rajasthan, India

Creative Commons Non Commercial CC BY-NC: This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 License (http://www.creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) which permits non-Commercial use, reproduction and distribution of the work without further permission provided the original work is attributed.
Digital transformation has become a pivotal driver of change in the hospitality industry, especially in culturally rich and tourist-centric regions like Rajasthan. By examining the current landscape, this study aims to provide insights into how digitalization is reshaping the hospitality industry in Rajasthan. This article explores the current status, potential opportunities, and prevailing challenges associated with the digital transformation of the hospitality sector in Rajasthan. It delves into the technological trends reshaping service delivery, customer engagement, and operational efficiency. The research further identifies the gaps in infrastructure, digital literacy, and policy frameworks that inhibit the seamless adoption of digital practices. It examines how the adoption of digital marketing and data analytics further enables targeted service offerings and strategic decision-making. Through a review of literature analysis, the study provides insights into how Rajasthan’s hospitality sector can leverage digital innovation to remain competitive while preserving its rich cultural heritage. The methodology used is a systematic review of literature with a sample size of 16 papers, which aims to synthesize existing academic literature to identify and analyze key trends, opportunities, and challenges shaping the hospitality industry in Rajasthan.
Digital transformation, customer engagement, operational efficiency
Introduction
A popular tourist destination in India, Rajasthan is known as the ‘land of kings’ and is well known for its magnificent forts, lavish palaces, lively festivals, and rich cultural legacy. From the sand dunes of the Thar Desert to the bustling bazaars of Jaipur and the serene lakes of Udaipur, Rajasthan offers a unique blend of historical grandeur and traditional hospitality. With its substantial contributions to infrastructure development, job creation and heritage preservation, Rajasthan’s tourism sector is vital to the state’s economy. Rajasthan is not an exception to the way that the world’s tourist industry has been changing recently due to its shift toward digital technology. The integration of digital tools and platforms into the tourism and hospitality sectors has transformed how tourists plan, experience, and share their journeys. From online bookings and digital payments to virtual tours and AI-powered customer service, digitalization is enabling a more seamless and personalized travel experience. Furthermore, government initiatives such as Digital India and the Rajasthan Tourism Policy 2020 have encouraged the adoption of smart tourism practices, especially in urban centers like Jaipur, Udaipur and Jodhpur. Over the past decade, the hospitality industry in the state has witnessed several evolving trends influenced by globalization, technological advancement, customer preferences, and policy interventions. Rajasthan’s tourism ranking has gone up from the eleventh position to the seventh position on national and international scales in 2023, all thanks to the government’s tourism policies (Mehta & Joshi, 2024).
Despite these advancements, the adoption of digital technologies in Rajasthan’s tourism sector remains uneven. While luxury hotels and urban establishments have embraced digital solutions, many rural and heritage properties face challenges related to infrastructure, digital literacy, and financial constraints. As the industry evolves, there is a pressing need to explore how digital transformation can be harnessed more inclusively and effectively across the state. This article seeks to analyze how digitalization and tourism interact in Rajasthan, stressing both the advantages and disadvantages of this change. It seeks to provide insights into how digital innovation can enhance service delivery, boost competitiveness, and preserve the state’s cultural heritage while ensuring sustainable and inclusive tourism development.
Although existing literature acknowledges the increasing influence of digital technology in tourism globally and in India, there is a notable lack of region-specific, empirical research examining how this transformation unfolds across diverse geographies and socioeconomic contexts within a single state like Rajasthan. Most studies to date focus on the broader benefits of digitalization or success stories in urban settings, overlooking the disparities in adoption between urban and rural tourism operators, and between large-scale businesses and small or heritage property owners. Furthermore, there is limited research on how digital technologies can be tailored to preserve cultural heritage while supporting sustainable and inclusive tourism development. This study addresses this gap by exploring the nuanced interaction between digitalization and tourism in Rajasthan, identifying barriers to widespread adoption, and offering strategies for inclusive digital transformation that align with both economic goals and heritage conservation imperatives.
Methodology
This study adopts a qualitative secondary research approach, relying on the analysis of existing literature, industry reports, government publications, and credible online sources to explore the digital transformation of the hospitality sector in Rajasthan. This study aims to evaluate the digital transformation in Rajasthan’s hospitality sector using a review of literature approach. Studies were selected based on relevance, quality, and novelty. The inclusion criteria for selecting articles in the literature review were carefully defined to ensure relevance and quality. Studies published between 2013 and 2024 were considered to capture recent and up-to-date findings. Only articles written in English were included to maintain consistency and clarity in understanding. The review focused on peer-reviewed journal articles and systematic reviews to ensure the credibility and scholarly value of the sources. The selected studies involved relevant populations and articles that specifically discussed digital tools, practices, and impacts in hospitality or tourism sectors relevant to India or similar developing regions. Terms like technologies like AI, cloud computing, IoT, CRM, PMS, digital marketing are used. Searches for relevant literature and data were conducted across multiple reputable academic databases to ensure comprehensive coverage. Scopus, Web of Science, Google Scholar, and JSTOR were among the search engines used.
Studies were excluded from the review that focused on sectors other than hospitality or if they did not explicitly address aspects of digital transformation. Additionally, studies published before 2013, those not written in English, and sources that were not peer-reviewed, such as editorials, opinion pieces, or news articles, were not considered.
Objectives
Review Process
A total of 97 articles were initially retrieved. After screening for duplicates, relevance, and quality, 16 studies were included in the final review (Figure 1).
Findings and Suggestions
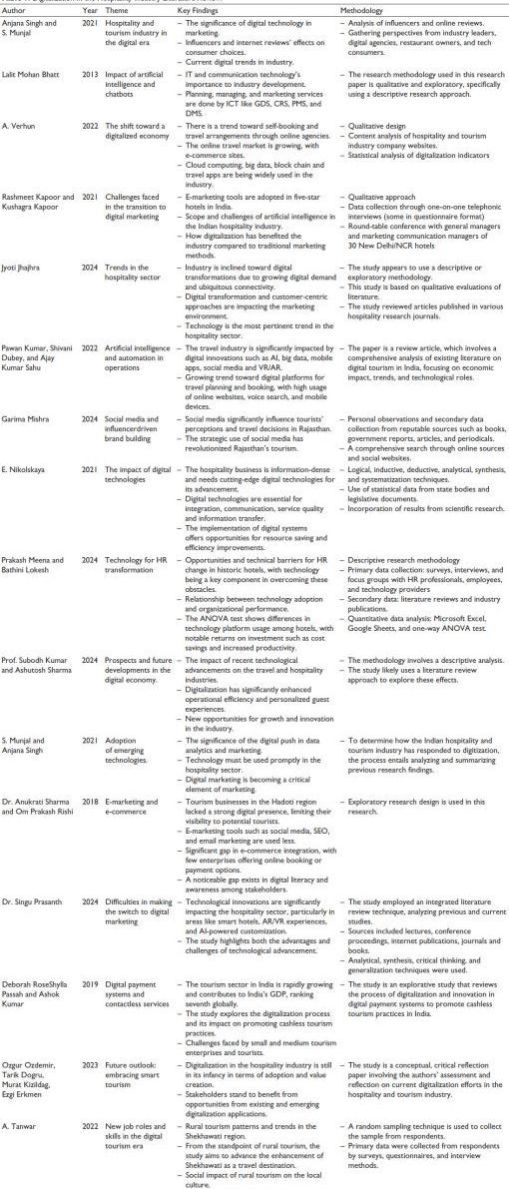
Recent literature underscores the growing significance of digital technologies in shaping marketing strategies, consumer engagement and operational efficiency within India’s hospitality and tourism sectors (Table 1). Digital tools such as GDS, PMS, CRS, and DMS have revolutionized planning, management, and service delivery (Bhatt, 2013), while advanced technologies such as AI, big data, cloud computing, and block chain are enabling personalized experiences and enhanced decision-making (Kumar & Sharma, 2024; Verhun, 2022). A consistent theme is the transition from traditional to digital marketing, particularly in luxury hotels, with increased adoption of e-marketing, social media, and influencer-based strategies to influence tourist behavior (Kapoor & Kapoor, 2021; Mishra, 2024). Digitalization also plays a vital role in improving internal operations, from HR functions in heritage hotels to guest satisfaction through mobile apps, automated systems, and integrated digital platforms (Meena & Lokesh, 2024; Singh & Munjal, 2021). Studies highlight its potential to boost customer retention, productivity, and global competitiveness (Munjal & Singh, 2021; Ozdemir et al., 2023). However, digital adoption is uneven across regions. Areas like Hadoti face infrastructural and awareness challenges (Sharma & Rishi, 2017), while rural tourism regions such as Shekhawati show untapped potential for digital-led cultural and employment growth (Tanwar, 2022). The need for training, financial literacy, and infrastructure remains critical, particularly for SMEs and rural stakeholders (Passah & Kumar, 2019; Prasanth, 2024).
Figure 1. PRISMA Flow Diagram.
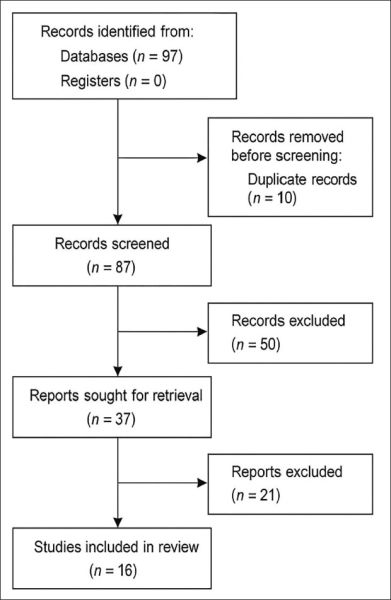
Table 1. Digitalization in the Hospitality Industry Literature Review.
To address these issues, it is recommended that the Rajasthan tourism and hospitality ecosystem prioritize targeted government support in the form of subsidies and digital transformation grants for SMEs. Enhancing digital infrastructure in rural areas through public–private partnerships is critical. Parallel to this, digital literacy and skills training for hospitality staff should be expanded through local academic institutions and tourism boards. Organizations can use a digital maturity model as a framework to evaluate their present state of digital transformation or maturity. It offers a methodical way to assess how successfully a company has incorporated digital technology into its procedures, values, and plans. Businesses may use the approach to prioritize projects, find gaps, and develop a digital progress plan. Heritage hotels should be guided to adopt hybrid service models that balance technology with personalized hospitality, preserving cultural authenticity while improving efficiency. Cybersecurity awareness and data protection protocols must be promoted through state-level guidelines, and affordable security solutions should be made accessible to small businesses. Overall, a regionally adaptive, equity-driven approach to digital transformation is essential to ensure Rajasthan’s hospitality industry thrives sustainably in the digital age.
Declaration of Conflicting Interests
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Funding
The authors disclosed receipt of the following financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Bhatt, L. M. (2013). Hospitality industry and the role of information technology. Paripex: Indian Journal of Research, 3(5), 1–3.
Kapoor, R., & Kapoor, K. (2021). The transition from traditional to digital marketing: A study of the evolution of e-marketing in the Indian hotel industry. Worldwide Hospitality and Tourism Themes, 13(2), 199–213.
Kumar, S., & Sharma, A. (2024). An era of digital transformation in the hospitality and tourism sector. Educational Administration: Theory and Practice, 30(4), 9422–9427. https://doi.org/10.53555/kuey.v30i4.4330
Meena, P., & Lokesh, B. (2024). Harnessing technology for HR transformation in hotel industry. International Journal of Multidisciplinary Research in Science, Engineering and Technology, 7(5), 9742–9754.
Mehta, P., & Joshi, P. (2024). Digital marketing and regional tourism: Opportunities for Rajasthan. International Journal of Tourism & Hospitality Reviews, 11(2), 29–41.
Mishra, G. (2024). Exploring innovative social media strategies for tourism promotion: A case study of Rajasthan. International Journal for Multidisciplinary Research, 6(4). https://doi.org/10.36948/ijfmr.2024.v06i04.24849
Munjal, S., & Singh, A. (2021). Going digital is the only way forward for the Indian hospitality and tourism industry. Worldwide Hospitality and Tourism Themes, 13(2), 291–295.
Ozdemir, O., Dogru, T., Kizildag, M., & Erkmen, E. (2023). A critical reflection on digitalization for the hospitality and tourism industry: Value implications for stakeholders. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management, 35(9), 3305–3321.
Passah, D. R. S., & Kumar, A. (2019). Cashless economy and digitalization of tourism & hospitality practices in India. SSRN Electronic Journal. http://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3308586
Prasanth, S. (2024). New technologies in the tourism and hospitality service sector. International Journal for Multidisciplinary Research, 6(1). https://doi.org/10.36948/ijfmr.2024.v06i01.12513
Sharma, A., & Rishi, O. P. (2017). A study on e-marketing and e-commerce for tourism development in Hadoti region of Rajasthan. Smart Innovation, Systems and Technologies, 83, 128–136.
Singh, A., & Munjal, S. (2021). How is the hospitality and tourism industry in India responding to the dynamic digital era? Worldwide Hospitality and Tourism Themes, 13(2), 163–167.
Tanwar, A. (2022). Role of tourism industry in employment generation in Rajasthan state. International Journal for Research Trends and Innovation, 7(6), 617–612.
Verhun, A. (2022). Digital tools for the development of the hospitality and tourism industry in the context of a digitized economy. Economic Affairs, 67(4s). https://doi.org/10.46852/0424-2513.4s.2022.20